What is a Listed Trust Service Provider?
A Listed Trust Service Provider is an entity that has executed the Marlin Trust Service Provider Agreement. A Listed Trust Service Provider is authorized to generate “Production Provisioning Packets”, i.e., keys and certificates for Marlin adopters (Clients and Service Providers) that do not wish to generate their own Marlin key material.
How does the MTMO issue development keys and test keys?
To encourage the rapid adoption of Marlin, the MTMO provides the Development Trust Infrastructure. There are two parts to the test infrastructure. First, adopters can download from the website a set of Common Test Keys that includes a test root, test Certification Authority, and sample credentials for services and clients. Later in development, an adopter can order a set of Adopter Test Keys. The Adopter Test Keys are from the same test root, and the values in the certificates are set by the Adopter to match what will be implemented in production.
How are keys and certificates provided for devices, applications, and services?
To acquire keys and certificates, an adopter must sign the appropriate MTMO agreement (for device or service provider) and pay the annual fee. Adopters have the option to generate their own keys by signing the Trust Service Provider Agreement, or to order them through a Listed Trust Service Provider. Client credentials (for devices or PC-software clients) can be provisioned either online via a service provider’s Personalization Server or at a factory before they hit the market. Server credentials must be manually configured by a service provider’s DRM administrators or developers.
What are the benefits of a delegated Certificate Authority (CA)?
The MTMO allows for the delegation of key management to adopters. The benefit of a delegated CA is that adopters can control the cost structure of key management either by establishing a CA in-house, outsourcing it to a service provider, or leveraging existing systems. This also allows adopters to design their own delegated trust hierarchy to meet individual business needs. For example, a large device manufacturer can design its trust hierarchy to have each geographical division be in charge of its own delegated CA; each geographical division can then delegate the CA responsibility to different sub-product divisions if the adopter chooses to. Alternatively, the device manufacturer can choose to have just one CA for all its devices and order all the device keys from a Listed Trust Service Provider.
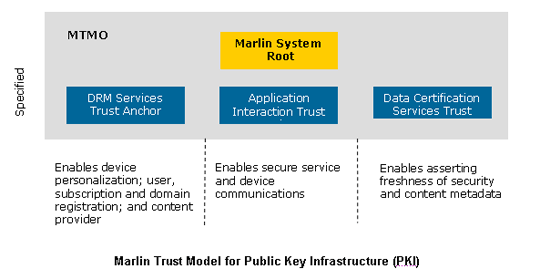
What are the key design objectives of the Marlin trust model?
The Marlin trust model consists of a single root of trust and delegated Certificate Authorities (CAs). The MTMO runs these trust anchors to allow interoperability between Marlin implementations.
How does the MTMO handle security breaches of devices and services?
Marlin is designed to support a variety of mechanisms that may be applied in the event of a security breach. These include revocation of devices and services, exclusion from content, and shunning access to services. The MTMO also employs both legal recourse and contractual remedies articulated in the MTMO agreements.
How does the MTMO enable interoperability?
The MTMO enables interoperability through:
- its ability to trust Marlin identities: the MTMO guarantees the certificates of principals used in all implementations are signed by common roots of trust and are generated according to trustable procedures. Any one entity can authenticate and trust the authenticity of any other entity by following the certificate chain to the common roots
- cryptographic mechanisms: the MTMO ensures that all keys and certificates adhere to a common specification
- compliance of implementations with a set of common specifications
- the use of a singly rooted PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) for device and service authentication
- a reporting body for keys and devices that are compromised.
What benefits does the MTMO provide to adopters of Marlin technology?
The MTMO provides a single trust management infrastructure that ensures interoperability between Marlin-compliant products and services. This allows renewable security to be implemented with minimum impact to consumers, client and service providers.
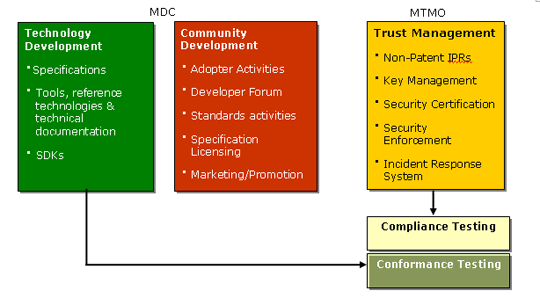
What is the MTMO’s relationship to the MDC? Why are they separate entities?
The MTMO and MDC (Marlin Developer Community) are separate entities specifically to keep technology development activities distinct and independent from the day-to-day activities associated with running a key management and trust services organization.
The MDC enables technology development to support the rollout of the Marlin ecosystem. It does this by developing and publishing the Marlin specifications, community code, tools, conformance test and development keys, and white papers for parties interested in evaluating and testing Marlin technology.
Note: All specifications and code available through the MDC are intended for internal and non-commercial purposes only.
The MTMO is the operational entity that grants commercial licenses for Marlin technology, and implements the Marlin trust model (including key management and certificate services) and renewability. The MTMO licensees have access to compliance and robustness rules for achieving certification, and other valuable tools and documents.
Note: Potential adopters of Marlin DRM, including device and service providers, are encouraged to evaluate Marlin technology before licensing the right to commercially deploy it.
For a more detailed division of labor between the 2 entities, see below
What is the MTMO’s role in Marlin?
The MTMO serves four key roles in Marlin:
- It grants non-patent IPR for commercial uses of Marlin technology.
- It provides key management and certificate services for Marlin products and services.
- It enforces compliance and robustness rules for Marlin products and services.
- It operates renewability services for the Marlin ecosystem.
